IoT in healthcare: 8 Examples from around the world

Demand for Internet of Things (IoT) solutions in healthcare is rising as healthcare systems around the world race to adopt the latest remote monitoring tools, devices and technologies that enable more efficient disease tracking, early diagnosis and treatment.
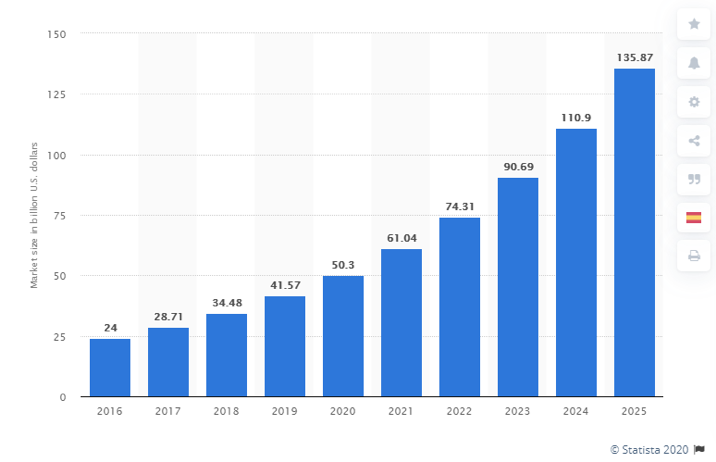
Healthcare-related IoT revenues are projected to more than double in market size over the next year five years to reach more than US$135 billion (€125 billion) by 2025, reports Shujaat Ali, the founder and chief-editor of Medical Travel Market.
Here is an insight into a handful of IoT solutions across all sides of the world.
1. Electronic vaccine intelligence network (eVIN) – India: India runs the largest vaccination programme in the world with 27 million new children immunised every year. eVIN is a mobile based technology developed by the UNDP and the Government of India to provide real-time logistics management across the vaccine cold chain. The app tracks the location, temperature (from SIM-enabled temperature loggers attached to cold chain equipment) and stock levels of vaccines, ensuring the supply is safe and reliable.
2.Skynet, Alibaba and Mobile Operators – China: China has invested heavily in healthcare industry IoT solutions, from digital health records to smartphone attachments reading EKGs and temperatures. Multiply this by 1.4 billion people, and you can sense the scale of big data available for data scientists to crunch on. During the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, Alibaba was able to implement a Skynet to over 100 cities within a week by leveraging smartphone apps and the power of mobile IoT connections. Alipay Health Code became an epidemic prevention and control health code system, which enabled large scale, real-time monitoring to support China in its efforts to stem the spread of the virus.
3.HearScreen smartphone audiometer – Africa: HearX group have pioneered a mobile app that offers a cost-effective and clinically validated means of screening for hearing loss by minimally trained professionals. It is estimated that 466 million people suffer from hearing loss worldwide, and this simple IoT solution is helping transform lives. The average test time is less than a minute, and it is proving popular in multiple settings, including schools, where educationally significant hearing loss can be detected early on through this simple screening method.

4. Electronic bed management system (eBMS) – Africa: Gauteng hospitals in South Africa manage an average of 27.7 million patients annually and often experience access pressures on the availability of beds. Gauteng health services introduced an innovative electronic Bed Management System, which enabled medical professionals to seamlessly identify the availability of beds across a cluster of sites. Results showed a 2-hour reduction in the wait time for a bed, providing patients in Emergency departments timely access to the care in the right setting.
5.Semtech LoRa fall detection device and network – Europe: Falling is a terrifying prospect for older people and monitoring patient falls is a critical safety measure used by healthcare providers. LoRaWAN provides a low power wide-area network (LPWAN) to detect falls amongst the elderly, connected to LoRa devices, up to 30 kilometres away. Movement data is collected from the sensors built into the LoRa technology and transmitted to the Cloud, where algorithms determine if the movement was a fall or not. Real-time alerts are sent to healthcare providers to reach patients quicker if they fall.
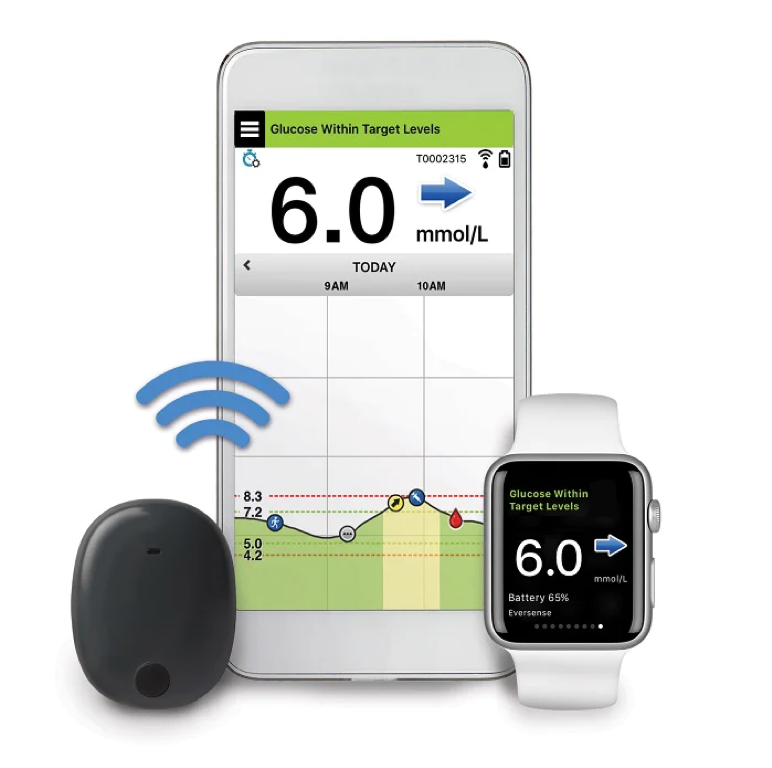
6.Eversense continuous glucose monitoring system – USA/Europe: The demand for innovations in diabetes control products is rising year on year as the prevalence of diabetes continues to increase. There are currently about 422 million people around the world with diabetes. The Eversense Continuous Glucose Monitoring System consists of an under-the-skin sensor, a smart transmitter (removable and rechargeable), and an app. This allows for up to 180 days of continuous monitoring and convenient real-time diabetes monitoring and management.

7.Kinsa smart thermometer – USA: A Kinsa smart thermometer can detect a temperature reading in 1 second and transmit this via Bluetooth to a mobile application. The app also tracks an individual’s symptoms and medications and keeps a history of temperature readings. Widespread use of smart thermometer sensors can help detect outbreaks and the spread of illnesses. Kinsa has been using smart thermometer data to build predictive models, which monitor fever hotspots across the country. While this doesn’t detect the spread of viruses such as COVID-19, it does detect early warning signs.
8.Vonage telemedicine APIs – USA: Using Vonage telemedicine APIs (application program interfaces), hospitals can deploy remote voice, SMS (short message service) and video collaboration tools between doctors and patients. This can be useful for engaging with and remotely monitoring patients that need isolation. Head-mounted smart-connected cameras can reduce the number of health professionals required to attend a patient in an isolation room. Connected remote monitoring with telemedicine can be used for home isolation as well.
Shujaat Ali, the founder and chief-editor of Medical Travel Market.
About the author
The Author is Shujaat Ali, the founder and chief-editor of Medical Travel Market, a UK-based digital media platform, committed to raising awareness about quality healthcare treatments and services across the world in an effort to bridge the gap between patients and leading healthcare providers worldwide.
Comment on this article below or via Twitter@IoTGN
