Hyperconvergence and computation at the edge: Part 3

Bob Emmerson
The adoption of edge and fog computing models is enabling enhanced efficiency, says Bob Emmerson. Data is generated at the edge and bringing processing power close to the source generates real-time information on which informed decisions and actions can be taken.This is an established trend that companies like VMware and Eurotech are advancing.
VMware provides a software-defined approach to hyperconvergence. It employs a hypervisor, aka a virtual machine monitor, in order to create and run virtual machines that deliver compute, storage and management in a tightly integrated software stack. Eurotech is an established supplier of enterprise-class Industrial IoT solutions that combine the company’s strengths on the Operational Technology (OT) side with the Information Technology (IT) expertise of ecosystem partners.
In the context of the trend towards edge computing, the two organisations have developed technology that employs VMware virtualisation technology, taking it from its regular role in the data centre / cloud and extending the benefits out to the edge of the OT network. Figure 1 (below) illustrates how it is deployed by Eurotech
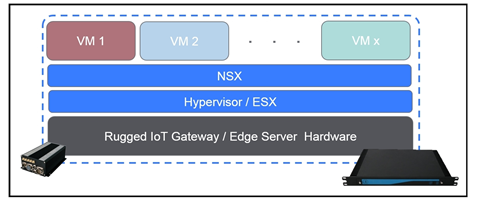
Figure 1. VMware ESX is hypervisor software that installs directly onto edge hardware. It enables physical resources to be partitioned into multiple VMs. NSX is networking software that enables VMs in different locations to communicate with each other.
This development raises the hyperconvergence bar. The consolidation of functional elements in data centres at the hypervisor level, together with federated management, reduces inefficiencies and minimises the total cost of ownership of the underlying IT infrastructure. In order to provide similar benefits at the edge, Eurotech has signalled plans to market edge server and IoT gateway products that are pre-installed with VMware virtualisation technology.
The implementation of VMware hypervisor technology on transportation-grade hardware, e.g. Eurotech’s rail certified fan-less edge server platform, was demonstrated at the VMworld 2017 Events in Las Vegas and Barcelona.
The planned products also address application scenarios where multiple computer systems are deployed, each of which enables a specific OT solution. These systems will typically involve different hardware and software implementations, which will inevitably result in logistic and support problems, thereby reducing operational performance and increasing maintenance costs.
Employing virtualisation technology at the edge addresses these issues by reducing the effort and cost for managing and maintaining the various systems. Typical multiple computer systems range from demanding transportation solutions such as rolling stock, construction & mining machines, marine vessels, smart energy / smart grid and retail.
That was a short take on a development that looks set to play a significant role on the OT side of hyperconverged infrastructures. That said, it is work in progress and we will surely see similar but alternative concepts. For example, in the next blog which focuses on secondary storage, dedicated OT hardware products at the edge are replaced by hyperconverged nodes running vSphere, which is VMware’s cloud computing virtualisation platform.
The author of this blog is Bob Emmerson, freelance IoT writer and commentator.
Comment on this article below or via Twitter @IoTGN
